Promising fantastic results for people with hyperpigmentation, tranexamic acid is becoming a go-to ingredient for dermatologists and skincare brands.
Before now, if you wanted to treat hyperpigmentation, you had to book a professional appointment. Now, thanks to advances in science, ingredients like tranexamic acid are giving prescriptions and procedures some stiff competition. Some studies even suggest it’s as effective as the prescription ingredient hydroquinone for melasma. (1)
In this blog post, we’ll explain what hyperpigmentation is, the science behind tranexamic acid, its efficacy and how to add this active ingredient to your everyday skincare routine.
What Is Hyperpigmentation?
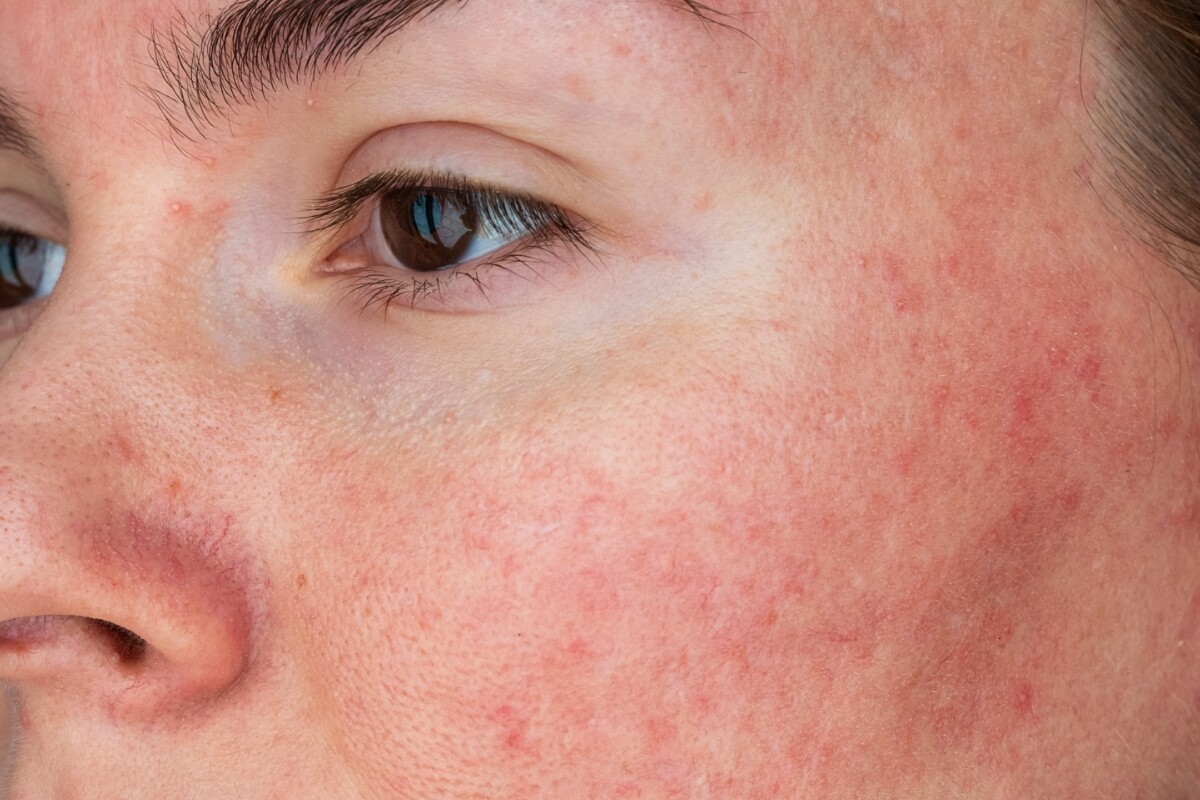
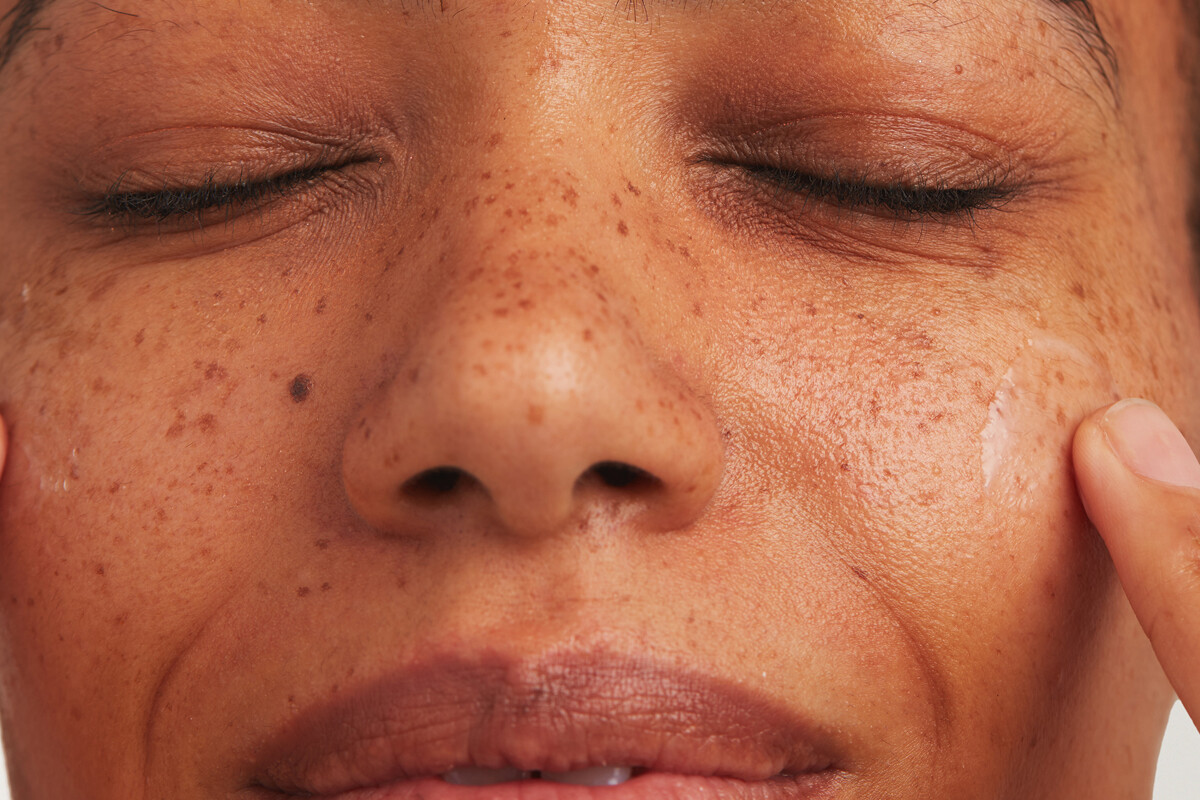
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin concern that – though harmless – isn’t straightforward to treat. It shows up as darkened brown or grey patches on the skin and can vary in size and severity depending on your unique skin.
Hyperpigmentation is a catch-all term to describe every type of skin discoloration, including post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, melasma, age spots, post-acne marks and dark spots.
The Role Of Melanin In Hyperpigmentation
Scientists believe these patches of uneven skin tone appear because of an overproduction of melanin—the pigment responsible for skin colour.
When your body produces too much melanin, it shows up as dark spots and hyperpigmentation.
Causes Of Hyperpigmentation
Factors like sun exposure, inflammation, hormonal changes such as during pregnancy or menopause, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation from acne, are all known to be triggers of hyperpigmentation.
This skin condition can affect anyone, but is more prevalent among people who are female with medium to darker skin tones. (2)
Tranexamic Acid: An Overview
What is Tranexamic Acid?
Tranexamic acid was originally used in medicine to control blood loss in major surgery, as well as for people who have heavy periods. (3)
It’s also been found to be an effective skincare ingredient for hyperpigmentation and age spots, either by taking it topically (applied on the skin) or orally (swallowed in pill form).
How Does Tranexamic Acid Work?
Tranexamic acid is believed to work by constricting small blood vessels in the skin and thereby reducing melanin (pigment) production. It interrupts the communication between skin cells called keratinocytes and melanocytes. This decreases the activity of an enzyme called tyrosinase, which is involved in melanin synthesis, leading to a brighter and more even complexion. (4)
Tranexamic acid targets the underlying causes of hyperpigmentation by disrupting melanin production, leading to a visible, long-term improvement to dark spots and overall skin tone.
The Efficacy of Tranexamic Acid in Treating Hyperpigmentation
Whether you’re treating melasma, sun damage, or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, tranexamic acid has been shown to lighten dark spots, reduce the intensity of skin pigmentation, and create a more even skin tone. Most study participants saw a difference in their skin in as little as 8 weeks, with a reported success rate of up to 80% for melasma patients, and 75% of participants with freckles. (5)
This active ingredient is also suitable for a wide range of skin types – including sensitive skin. It’s a gentle yet effective way to tackle your hyperpigmentation skin goals, or for long-term hydroquinone users during their recommended break.
Research and Studies on Tranexamic Acid for Hyperpigmentation
Clinical Studies on Tranexamic Acid for Hyperpigmentation
A recent study from 2022 found that tranexamic acid significantly reduced melasma in patients after 12 weeks, with some patients seeing results as early as two weeks into treatment. (6)
Another study published in the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology examined topical tranexamic acid on Asian patients with melasma. Results showed that applying tranexamic acid to the skin led to a significant improvement in melasma lesions and overall skin tone. (7)
Tranexamic acid has also shown promising results for post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). A study conducted by the Japanese Dermatological Association found that the use of tranexamic acid cream reduced post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in patients who had had dermatological procedures. (8)
How To Add Tranexamic Acid To Your Skincare Routine
Tips From Dermatologists On Treating Hyperpigmentation Effectively
– Combine It With A Personalised Formula: When used together with active ingredients, they can enhance the effect of the other, evening out the overall skin tone. Just make sure that you consult a dermatology expert to make sure the combination is right for your skin.
– Incorporate Vitamin C: Combining tranexamic acid with Vitamin C can give your skin goals a powerful boost. Look for 15% ascorbic acid, as this concentration is highly potent – while still suiting most skin types.
– Try Niacinamide: Niacinamide is a form of Vitamin B3 that also helps reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation and brighten the overall complexion.
Tranexamic Acid vs. Other Ingredients For Hyperpigmentation
Comparing Tranexamic Acid With Hydroquinone For Hyperpigmentation Treatment
Prescription hydroquinone is the gold standard treatment for hyperpigmentation. It’s known for its ability to lighten dark spots and even out your overall complexion.
Hydroquinone works by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which is involved in melanin production. On the other hand, tranexamic acid reduces tyrosinase’s activity and constricts small blood vessels in the skin – which targets and fades existing hyperpigmentation.
On the whole tranexamic acid is also gentler. It suits a wider range of skin types, including sensitive skin, and it can be used safely for long periods without breaks – unlike hydroquinone. (9)
How It Compares With Vitamin C for Dark Spots
Vitamin C (L-ascorbic acid) can even out skin tone and reduce hyperpigmentation. However, it works in a different way.
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that helps eradicate dullness while enhancing the performance of your broad-spectrum sunscreen. It also protects your skin from free radical damage. All of these benefits help slow down the production of melanin.
Studies have shown that tranexamic acid can produce faster and more dramatic results for melasma than Vitamin C. In one tranexamic acid study, participants saw a significant reduction in pigmentation intensity after 12 weeks, while Vitamin C users noticed less improvement. (10)
Vitamin C is also useful for enhancing the SPF (Sun Protection Factor) in your sunscreen. Sun damage is a key culprit for darkening hyperpigmentation – so in this case, there’s no such thing as too much protection.
You don’t have to choose between the two ingredients. In fact, incorporating both these ingredients into your routine isn’t just safe for most people, it can help fade dark spots faster too.
Conclusion
With its proven ability to inhibit melanin production and promote a more even complexion, it’s no wonder tranexamic acid is cropping up in more and more skincare products for hyperpigmentation.
As always, no two people’s skin journeys will look the same. Find out what formulas are suitable for your skin by visiting our website.
References
1. Manasa Shettisara Janney, Radhakrishnan S, Rajeshwari Dabas, Lal S, Das NM, Godara SK. A Randomized Controlled Study Comparing the Efficacy of Topical 5% Tranexamic Acid Solution versus 3% Hydroquinone Cream in Melasma. PubMed. 2019 May 7;12(1):63–7.
2. Thawabteh AM, Jibreen A, Karaman D, Thawabteh A, Karaman R. Skin Pigmentation Types, Causes and Treatment—A Review. Molecules [Internet]. 2023 Jan 1;28(12):4839. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/28/12/4839
3. Franchini M, Mannucci PM. The never ending success story of tranexamic acid in acquired bleeding. Haematologica. 2020 Mar 26;105(5):1201–5.
4. Batra J, Brar B, Kumar S, Arora H. Tranexamic acid in melasma: Comparative evaluation of therapeutic efficacy of oral tranexamic acid versus its transepidermal administration. Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery. 2022;15(4):394
5. Ebrahimi B, Naeini FF. Topical tranexamic acid as a promising treatment for melasma. Journal of Research in Medical Sciences : The Official Journal of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences [Internet]. 2014 Aug 1;19(8):753–7. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4235096/
6. González-Molina V, Martí-Pineda A, González N. Topical Treatments for Melasma and Their Mechanism of Action. The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology [Internet]. 2022 May 1 [cited 2024 Jun 17];15(5):19–28. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9122278/
7. Optimizing Melasma Management With Topical Tranexamic Acid: An Expert Consensus [Internet]. JDDonline – Journal of Drugs in Dermatology. Available from: https://jddonline.com/articles/optimizing-melasma-management-with-topical-tranexamic-acid-an-expert-consensus-S1545961623P0386X/
8. Yeong Hee Cho, Jung Eun Park, Do Sung Lim, Jung Sup Lee. Tranexamic acid inhibits melanogenesis by activating the autophagy system in cultured melanoma cells. Journal of dermatological science. 2017 Oct 1;88(1):96–102.
9. Manasa Shettisara Janney, Radhakrishnan S, Rajeshwari Dabas, Lal S, Das NM, Godara SK. A Randomized Controlled Study Comparing the Efficacy of Topical 5% Tranexamic Acid Solution versus 3% Hydroquinone Cream in Melasma. PubMed. 2019 May 7;12(1):63–7
10. Eram H, Menon A, Kamath P, Goel S, Babu A. A split face comparative study of safety and efficacy of microneedling with tranexamic acid versus microneedling with Vitamin C in the treatment of melasma. Indian Dermatology Online Journal. 2019;0(0):0.
Ash Sharma
Dr Ashwin Sharma is a medical doctor and writer with a particular interest in health technology, artificial intelligence and medical weight loss. He completed his training at the University of Leicester and Imperial College London, and has since been exploring the intersections of medicine, technology, and communication.