Topical niacinamide has a large fanbase in the dermatology world. It’s been proven in study after study to be a key ingredient to tackle symptoms of acne, hyperpigmentation and premature ageing (also known as photoageing). Whether it’s in your serum, moisturiser or personalised formula, if you’ve seen this ingredient name on the side of your skincare bottle, and it’s raised some questions, you’ve come to the right place.
While this powerful ingredient has plenty of potential to do incredible things, it’s more of a supporting player than a solo star. Though it will help improve almost any skin concern, niacinamide needs other ingredients working alongside it (like retinoids, salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, etc) to achieve significantly better results. (1) Nonetheless, here’s what you might expect after you start using it, how long it takes to see results, and why it’s so beneficial for your skin.
What is Niacinamide?
Topical niacinamide is a form of Vitamin B3. It’s a water-soluble vitamin that works with the natural substances in your skin to:
– Reduce the appearance of enlarged pores
– Correct uneven skin tone
– Smooth the look of fine lines
– Enhance skin radiance
– Regulate sebum production
– Help strengthen the skin barrier
Niacinamide is an antioxidant. Like Vitamin C, the antioxidant properties can help reduce the risk of oxidative stress from the environment (2) and minimise sun damage when it’s combined with a broad-spectrum sunscreen in the morning. (3)
Skin Benefits of Niacinamide
Anti-inflammatory Properties
Niacinamide is particularly effective for calming irritated skin, smoothing rough skin texture and reducing redness for people with sensitive, reactive or acne-prone skin. (4)
Minimises Pores
It helps regulate oil production, which can reduce the appearance of visible pores for people with skin conditions like acne. (2)
Improves Skin Barrier Function
Niacinamide also helps strengthen the skin’s natural barrier, which keeps the skin hydrated by reducing TEWL (trans epidermal water loss). This in turn prevents overall moisture loss, to help your skin protect itself against environmental damage. (4)
Brightens Skin
By reducing the appearance of dark spots, age spots and hyperpigmentation generally, using niacinamide consistently helps promote a more even skin tone.
Combining it with brightening actives and broad-spectrum sunscreen can reduce the effects of sun-induced skin ageing and pigmentation. (3) We outline which ingredients work best to tackle this condition below.
Slows Premature Ageing
It improves the look of fine lines, making it helpful if your main skin goal is anti-ageing.
Suits All Skin Types
Whether you have dry skin, mature skin, balanced skin, acne-prone skin, and/or oily skin, niacinamide is suitable for all skin types. The effects of niacinamide are visible for all skin concerns, too. (5)
What To Know Before Adding Niacinamide To Your Skincare Routine
Incorporating a niacinamide skincare product into your skincare routine is straightforward, and doesn’t require too much thought.
Fortunately, you can use almost any skincare ingredient in combination with niacinamide without issues. These compatible ingredients include:
– Hyaluronic acid, e.g. our Hydrating Hyaluronic Acid + Vit B5 Serum
– Retinol and retinoids, like adapalene and tretinoin
– AHAs like glycolic acid, lactic acid and mandelic acid
– BHAs like salicylic acid
– Benzoyl peroxide
– Antioxidants, e.g. our Vitamin C 15% Fresh Batch Ascorbic Acid
– Azelaic acid, e.g. our Clarifying Azelaic Acid 12%/15% Cream
Before: How To Add Niacinamide To Your Skincare Routine
Step 1 Cleanse
Start with a gentle cleanser like Balancing Glycerin Gel Cleanser to remove dirt, makeup, sunscreen and impurities.
At night: Repeat one more time to ensure you remove all traces. This is often referred to as a double cleanse.
Step 2 Treat
Apply a few drops of niacinamide serum to your skin after cleansing, gently patting it in.
At night: Dermatica’s personalised formulas contain niacinamide, and this is the step in your skincare routine when you would use it.
Step 3 Moisturise
Follow with Soothing Centella Gel Moisturiser to lock in the hydrating ingredients, maintain healthy skin and strengthen your skin barrier.
Tip: It’s fine to have multiple skincare products containing niacinamide in your skincare routine, including your serum, eye cream, personalised formula and moisturiser.
Step 4 Protect
During the day, always finish your skincare routine by applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen like SPF50 Photodamage Defence Sunscreen. This helps protect your skin from UV damage, premature skin ageing and skin cancer.
After: When To Expect Results From Niacinamide
Less Acne
Many people notice a significant decrease in acne and breakouts after just a few weeks of using niacinamide. Its anti-inflammatory effects and management of oil production helps keep your skin clearer and smoother.
Improved Skin Texture
Users notice a smoother skin texture and reduction in pore size after a few weeks of use. The skin also looks more refined and even.
Brightening of Melasma, Dark Spots and Sun Spots
In studies on Japanese women, results show that niacinamide has the ability to significantly decrease hyperpigmentation, and brighten the skin tone after 4 weeks of use. (6)
For the treatment of melasma, other studies have reported niacinamide taking up to 8 weeks to see results. (7)
People tackling hyperpigmentation, melasma, dark spots, sun damage and age spots often notice a more uniform complexion. Especially when combined with brightening active ingredients like:
– Vitamin C
– Retinoids like tretinoin and adapalene
– Azelaic acid
– Tranexamic acid
– Hydroquinone
Conclusion
From reducing inflammation and minimising pores to brightening dark spots and fighting early signs of skin ageing, niacinamide can be a valuable addition to almost anyone’s skincare routine.
But as mentioned at the start, niacinamide shouldn’t be the only ingredient you use to treat your skin concerns. It’s much more effective when used in combination with other active ingredients. For more advice about which ingredients work best for your individual skin type, visit our website.
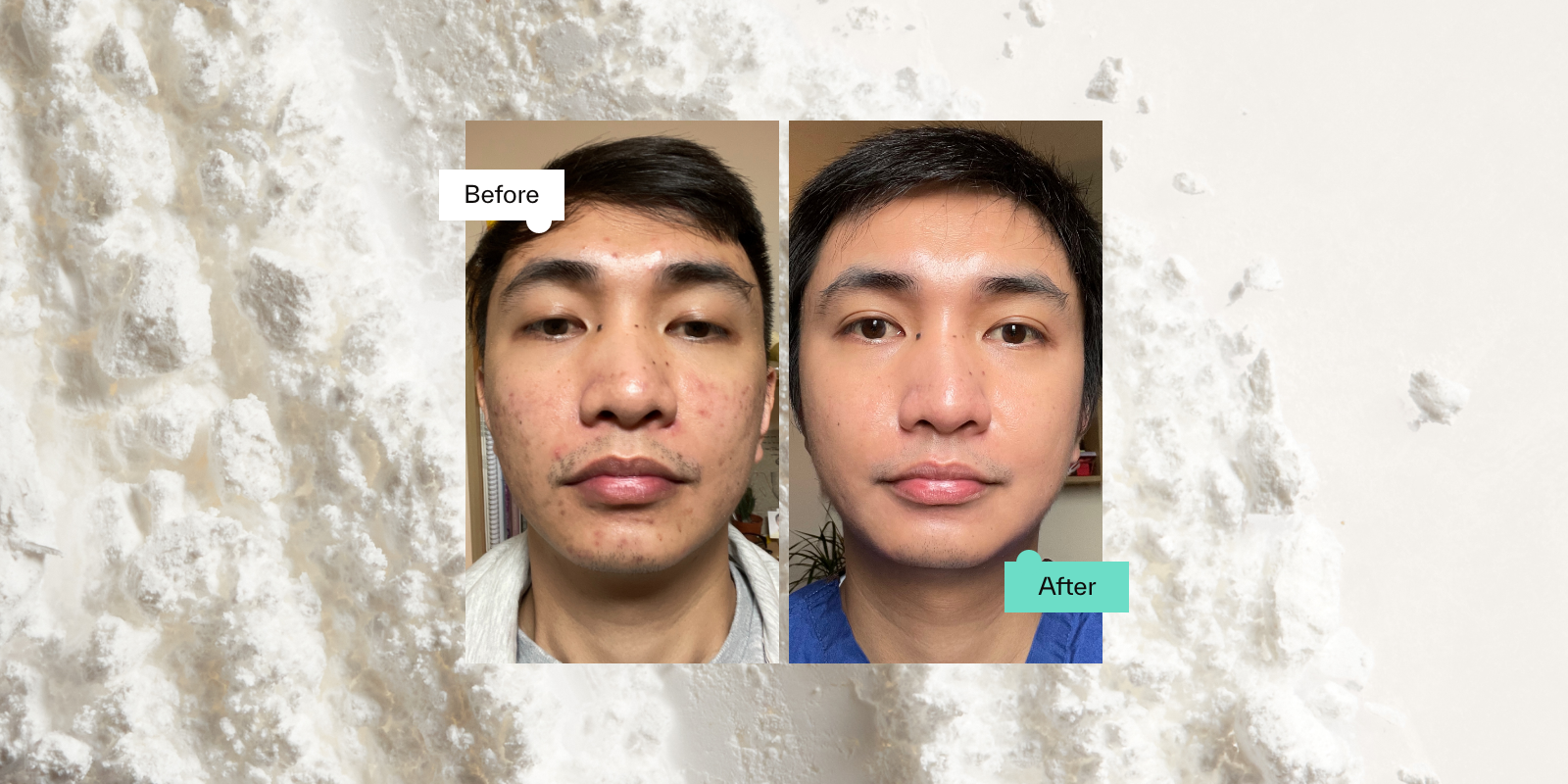
Niacinamide Before And After Image
Dermatica Customer: Michael
Skin concern: Acne
Treatment ingredients: Tretinoin, Niacinamide, Clindamyicn
Treatment length: 3 months
References
1. Levin J, Momin SB. How Much Do We Really Know About Our Favorite Cosmeceutical Ingredients? The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology [Internet]. 2010 Feb 1;3(2):22–41. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2921764/
2. Boo YC. Mechanistic Basis and Clinical Evidence for the Applications of Nicotinamide (Niacinamide) to Control Skin Aging and Pigmentation. Antioxidants [Internet]. 2021 Aug 21;10(8):1315. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8389214/“>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8389214/”>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8389214/
3. Wohlrab J, Kreft D. Niacinamide – Mechanisms of Action and Its Topical Use in Dermatology. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology. 2014;27(6):311–5.
4. Marques C, Hadjab F, Porcello A, Lourenço K, Scaletta C, Abdel-Sayed P, et al. Mechanistic Insights into the Multiple Functions of Niacinamide: Therapeutic Implications and Cosmeceutical Applications in Functional Skincare Products. Antioxidants [Internet]. 2024 Apr 1;13(4):425. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3921/13/4/425
5. Madaan P, Sikka P, Malik DS. Cosmeceutical Aptitudes of Niacinamide: A Review. Recent Advances in Anti-Infective Drug Discovery. 2021 Nov;16(3):196–208.
6. Hakozaki T, Minwalla L, Zhuang J, Chhoa M, Matsubara A, Miyamoto K, et al. The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer. The British Journal of Dermatology [Internet]. 2002 Jul 1 [cited 2020 Feb 16];147(1):20–31. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12100180
7. Navarrete-Solís J, Castanedo-Cázares JP, Torres-Álvarez B, Oros-Ovalle C, Fuentes-Ahumada C, González FJ, et al. A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial of Niacinamide 4% versus Hydroquinone 4% in the Treatment of Melasma. Dermatology Research and Practice. 2011;2011:1–5.
Cat Hyatt
Dr Cat Hyatt is a GP, working as Clinical Content Lead for Dermatica. She has a special interest in medical content and making healthcare information accessible and understandable for all.